What Is Magnetic Torque?
Definition of magnetic torque
Magnetic torque is an important and fundamental concept in electromagnetism that describes the rotational effect of a magnetic field on an object. In short, a magnetic torque is a rotational force caused by the interaction of an object’s magnetic torque with the surrounding magnetic field.
Mathematically, the magnetic torque (τ) can be expressed by the following equation:
τ=μ×B
where τ is the magnetic torque, μ is the magnetic torque of the object, and B represents the surrounding magnetic field. This expression reveals the interrelationship between the magnetic torque and the magnetic field, which in turn leads to the rotational force on the object.
Fundamentals of the interaction of magnetic fields and magnetic torques
A magnetic field is a field that is generated by moving charges and creates a force in space. A magnetic torque, on the other hand, is an inherent magnetic property of an object; it is a vector whose direction is from the object’s south pole to its north pole.
When a magnetic torque is placed in an external magnetic field, the magnetic field exerts a torque that causes the torque to try to align itself with the direction of the magnetic field. The magnitude and direction of this moment is determined by the angle between the magnetic torque and the magnetic field. According to the right-hand rule, the direction of the torque is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field and the magnetic torque.
The interaction of the magnetic field and the magnetic torque has important applications not only in fundamental physics, but also plays a key role in a variety of technological and engineering applications, such as electric motors, generators, and magnetic resonance imaging. A deeper understanding of this fundamental principle can help to optimize and innovate many modern technological applications of electromagnetism.
Right-hand rule for the direction of the magnetic torque
The right-hand rule is a rule for determining the direction of vectors and is often used to describe the direction of magnetic fields, currents, and torques. For the direction of magnetic torques, the right-hand rule can be succinctly stated.
Steps in the application of the right-hand rule to the direction of the magnetic torque:
- Holding the magnetic torque: Hold the magnetic torque of an object with your right hand so that your index finger is pointing in the direction of the magnetic torque, indicating where the torque is pointing.
- Extend your thumb: Point the thumb of your right hand in the direction of the magnetic field to indicate the direction of the magnetic field.
- Middle finger perpendicular to index finger and thumb: Hold the middle finger of your right hand perpendicular to your index finger and thumb, which indicates the direction of the magnetic torque.
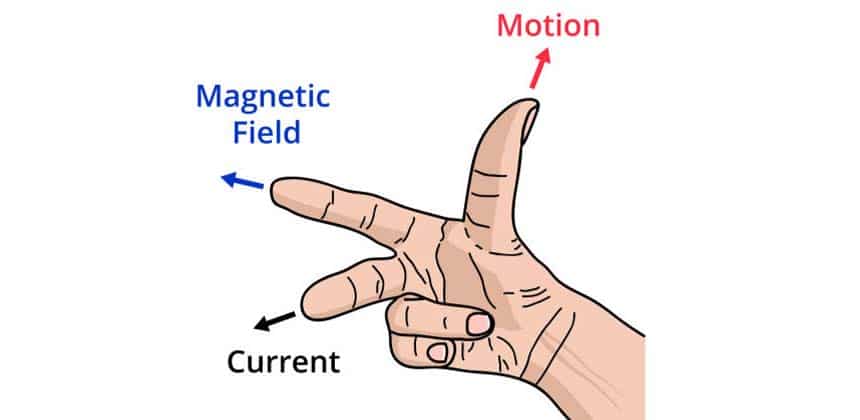
According to the right-hand rule, the direction of the magnetic torque is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic torque and the magnetic field. Specifically, if you use the index finger of your right hand to indicate the direction of the magnetic torque of an object and the thumb to indicate the direction of the magnetic field, then the direction of the magnetic torque will be indicated by the middle finger.
This rule applies to describing the direction of the torque on an object in a magnetic field, such as in motors and generators, and it helps to understand how a magnetic field produces torque on a rotating body.
Areas of application of magnetic torque
Principle of motor operation
Magnetic torque plays a key role in motors. In a DC motor, a current passes through a coil to produce a magnetic field, and this field interacts with permanent magnets or other magnetic fields in the motor, causing the coil to rotate by a magnetic torque. This rotating motion is caused by the magnetic torque created by the interaction between the magnetic field and the current.
In an AC motor, the alternating current causes a change in the direction of the magnetic field in the motor, resulting in a rotating magnetic field. This rotating magnetic field interacts with the rotor in the motor to produce a magnetic torque that pushes the rotor to turn and drive mechanical devices such as fans, pumps, and transmissions.
Magnetic torque applications in generators
In a generator, magnetic torque is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. As the rotor of the generator rotates, it interacts with the magnetic field and produces a magnetic torque. This magnetic torque causes the wire to move in the magnetic field, which generates an electric potential in the wire. In this way, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy and the generation of electricity is realized.
The principle of operation of a generator is based on electromagnetic induction, in which the magnetic torque plays a key role. This application makes the generator an important device capable of providing energy for our electrical needs.
The application of magnetic torque in pumps usually involves magnetically driven pumps(MP Magnetic Drive Pump), which are special pump systems that do not require the use of mechanical seals. In this type of pump system, the magnetic torque is used to transmit power without the need for a direct connection between the shaft of the pump and the shaft of the motor, thus preventing the problem of possible leakage in the pump system.


Key Influences on Magnetic Torque
Effect of magnetic torque strength
The magnetic torque is a vector quantity that describes the magnetic properties of an object and the direction of the magnetic field. The strength of the magnetic torque directly affects the magnitude of the magnetic torque. When the strength of the magnetic torque increases, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the object also increases. In equipment such as motors and generators, the efficiency and performance of the equipment can be improved by increasing the strength of the magnetic torque.
Effect of magnetic field strength on magnetic torque
The strength of the magnetic field is the key factor in the magnetic force that the field exerts on an object. The greater the strength of the magnetic field, the greater the magnitude of the magnetic torque. This means that increasing the strength of the magnetic field enhances the effect of the magnetic torque, thereby increasing the sensitivity and output of the device. In electromagnetic devices, precise control of device performance can be achieved by adjusting the strength of the magnetic field.
The importance of the angle between the magnetic torque and the magnetic field
The angle is the key factor in the magnitude of the magnetic torque and is determined by the angle between the magnetic torque and the magnetic field. The magnitude of the magnetic torque is determined by the equation τ = μ×B x sin(0), where 0 is the angle between the magnetic torque and the magnetic field. When the magnetic torque is perfectly aligned with the direction of the magnetic field, sin(0) = 1 and the magnetic torque achieves its maximum value. Conversely, if the magnetic torque is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field (0 = 909), then sin(0) = 0 and the magnetic torque is zero.
Therefore, adjusting the angle between the magnetic moment and the magnetic field can effectively control the magnitude of the magnetic moment. In practice, the adjustment of this angle can be achieved by adjusting the magnetic field or adjusting the direction of the magnetic moment to optimize the performance and response of the device.
Summary
This post summarizes the concept of magnetic torque as a description of the rotational force on an object in a magnetic field, resulting from the interaction of the object’s magnetic torque with the surrounding magnetic field. Its direction follows the right-hand rule and depends on the strength of the magnetic torque, the strength of the magnetic field, and the angle between the torque and the magnetic field. In practice, magnetic torques are used to drive rotational motion in electric motors and to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy in generators.
AOBL not only provides MP Magnetic Drive Pump, but also provides other models of magnetic pumps which can be purchased according to your different needs. Not only that it also provides AODD Pump, EODD Pump, sanitary diaphragm pump, screw pump, vertical centrifugal pump and chemical pump. If you have any questions, please consult us.