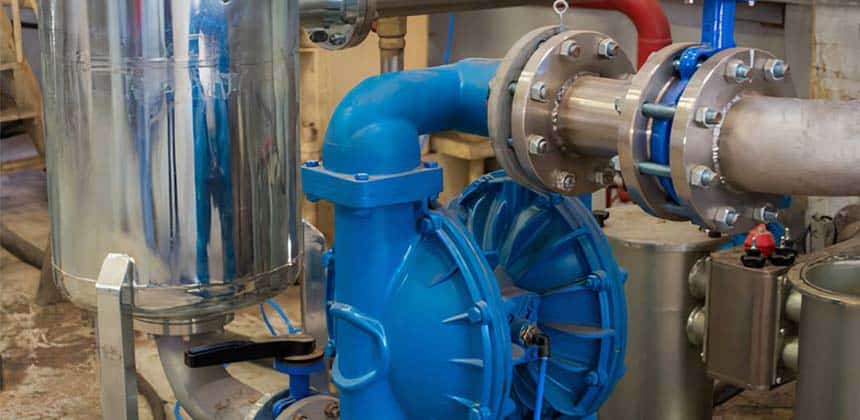
Types of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps are a type of pump that moves fluid by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and then forcing it out. This is in contrast to centrifugal pumps, which move fluid by imparting a rotating motion to the fluid.
Positive Displacement Pump Working Principle
Positive displacement pumps mechanically “trap” liquid in a fixed volume and then force it out. Unlike centrifugal pumps, it delivers a fixed volume of liquid in each operating cycle and is not affected by changes in system pressure, making it suitable for high viscosity or where precise flow control is required.
Key differences between positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps
The main difference between a positive displacement pump and a centrifugal pump is how they move fluid. Positive displacement pumps move fluid by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and then forcing it out. Centrifugal pumps move fluid by imparting a rotating motion to the fluid, which causes the fluid to flow outward.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps:
| Feature | Positive Displacement Pump | Centrifugal Pump |
| How they move fluid | Trap a fixed volume of fluid and then force it out | Impart a rotating motion to the fluid, which causes the fluid to flow outward |
| Flow rate | Constant flow rate | Variable flow rate |
| Head | High head | Low head |
| Applications | Pumping fluids with high viscosity or that contain solids, precise dosing, dispensing fluids | Pumping large volumes of fluid, low viscosity fluids |
| Advantages | Can pump fluids with high viscosity or that contain solids, can deliver a precise amount of fluid each time, relatively compact and lightweight | More efficient at low viscosity fluids, less expensive, less prone to wear and tear |
| Disadvantages | More expensive, more prone to wear and tear, can be noisy | Not as efficient at high viscosity fluids, not as well-suited for pumping fluids that contain solids |
In general, positive displacement pumps are better suited for applications where a precise amount of fluid needs to be pumped, such as in metering or dispensing applications. Centrifugal pumps are better suited for applications where large volumes of fluid need to be pumped, such as in water or wastewater treatment plants.
Common types of positive displacement pumps
The general term for positive displacement pumps is volumetric pumps. This is because they move a fixed volume of fluid with each cycle of operation.
There are two main types of positive displacement pumps: reciprocating and rotary.
- Reciprocating pumps use a piston, diaphragm, or plunger to move the fluid. The piston or plunger moves back and forth in a cylinder, trapping a fixed volume of fluid each time. The fluid is then forced out of the cylinder when the piston or plunger moves to the other end.
- Rotary pumps use rotating gears, vanes, or lobes to move the fluid. As the gears, vanes, or lobes rotate, they trap a fixed volume of fluid and then force it out.
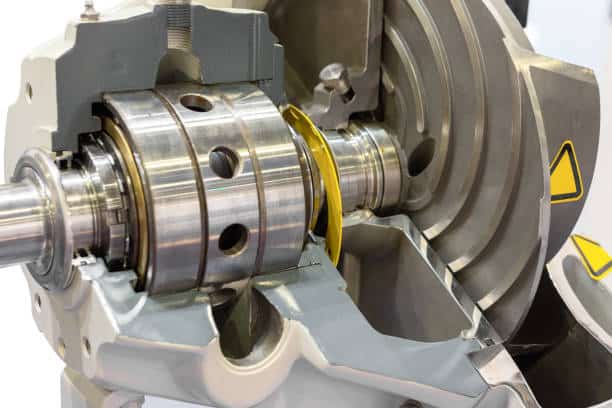

Reciprocating Pumps
Piston Pump
Piston pumps utilize the reciprocating motion of the piston in the pump cylinder to realize the suction and discharge of liquid through the check valve. Suitable for high-pressure conditions, commonly used in chemical metering, liquid quantitative injection.
Plunger Pump
Plunger Pump is similar to plunger pump, but the seal does not move with the plunger, more suitable for high-pressure working conditions, widely used in industrial cleaning, high-pressure water injection system.
Diaphragm Pump
Diaphragm pump through the reciprocating deformation of the flexible diaphragm to promote the liquid, sealing performance is excellent, suitable for corrosive, easy to leak or toxic liquid transportation occasions, widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, food and other industries.
Rotary Pumps
Gear Pump
By a pair of meshing gears rotating to drive the liquid movement, simple structure, commonly used in lubrication systems, hydraulic equipment, fuel delivery and other fields.
Screw Pump
Screw pump with the help of one or more screws rotating, in the pump cavity to continuously advance the liquid, suitable for high viscosity or containing certain particles of liquid, such as crude oil, chemical slurry.
Vane Pump
The slide in the rotor extends and fits the pump casing under the action of centrifugal force, forming a closed volume to transmit liquid, commonly used in hydraulic systems or low viscosity liquid transportation.
Roots Pump
By two synchronized rotation of the “impeller” to promote the liquid, non-contact, low shear, for food, medicine and other high hygiene requirements or sensitive materials scene.
Hose Pump / Peristaltic Pump
Peristaltic fluctuation through the roller compression hose, push the liquid forward, especially suitable for clean, measurement, laboratory and other requirements of accurate, pollution-free transportation process.
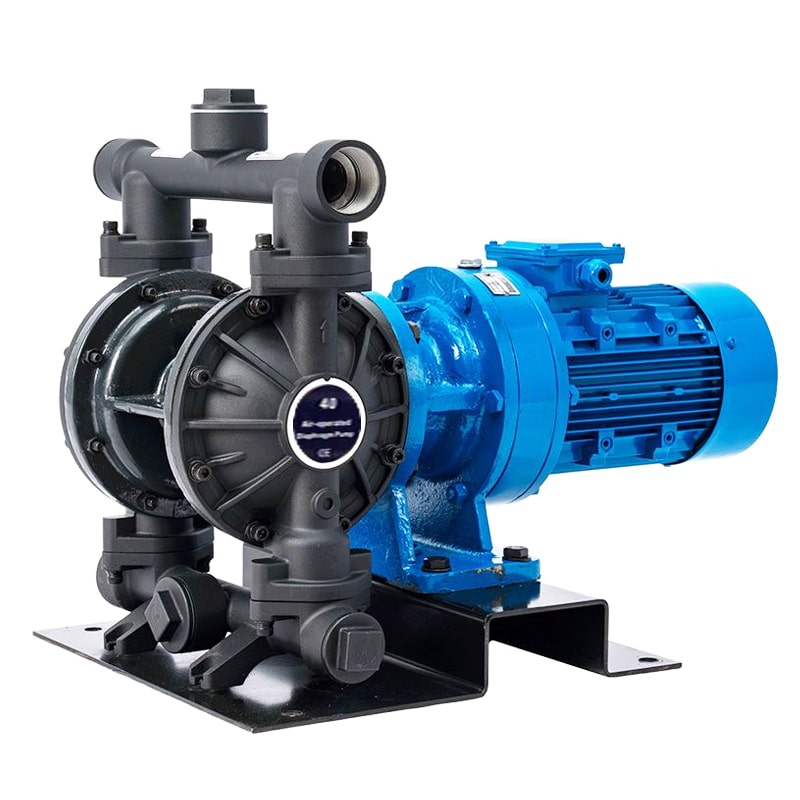
Advantages of AODD Pump and EODD Pump in positive displacement pumps
Air-operated double diaphragm pumps(AODD) are powered by compressed air. This makes them portable and easy to use, as they do not require an external power source. They are also relatively inexpensive. However, air-operated double diaphragm pumps can be noisy, and they may not be as efficient as electric diaphragm pumps at pumping large volumes of fluid.
Electric diaphragm pumps(EODD) are powered by an electric motor. This makes them more versatile than air-operated double diaphragm pumps, as they can be used in applications where compressed air is not available. They are also typically more efficient than air-operated double diaphragm pumps at pumping large volumes of fluid. However, electric diaphragm pumps are more expensive than air-operated double diaphragm pumps, and they may require more maintenance.
AOBL offers not only air operated diaphragm pumps, but also electric diaphragm pumps, KES25 1″ Plastic Diaphragm Pump and Electric Diaphragm (EODD) Pump are good choices.


Here is a table summarizing the advantages of AODD pump and EODD pump:
| Feature | Pneumatic Diaphragm Pump | Electric Diaphragm Pump |
| Power source | Compressed air | Electric motor |
| Portability | Portable | Not portable |
| Cost | Inexpensive | More expensive |
| Noise level | Noisy | Quieter |
| Efficiency | Less efficient at pumping large volumes of fluid | More efficient at pumping large volumes of fluid |
| Maintenance | Requires less maintenance | Requires more maintenance |
Overall, the best type of diaphragm pump for a specific application will depend on the specific requirements of the application. If portability and low cost are important factors, then a pneumatic diaphragm pump may be a good choice. If efficiency and quiet operation are important factors, then an electric diaphragm pump may be a good choice.
Limitations of positive Displacement Pump
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Overpressure Risk | Positive displacement pumps continue to deliver flow even if the outlet is blocked. Without a pressure relief valve, this can damage equipment. |
| 2. Higher Cost | Compared to centrifugal pumps, many PD pumps (e.g., piston or screw pumps) are more expensive to manufacture and maintain. |
| 3. Pulsating Flow | Certain types, like piston or diaphragm pumps, produce a pulsating flow, often requiring a pulsation dampener to smooth the output. |
| 4. Sensitivity to Solids | Gear and vane pumps can be damaged or clogged by fluids containing solid particles unless specifically designed for such use. |
| 5. Wear and Tear | Due to the close mechanical tolerances and constant contact, wear is more pronounced, depending on the fluid and operating conditions. |
| 6. Speed Limitations | Running at high speeds may lead to excessive wear or cavitation; most PD pumps are designed for lower RPM operation. |
| 7. Start-up Requirements | Some PD pumps must not run dry. They require pre-filling with fluid to avoid damage to internal components. |
Some common failures of positive displacement pumps
- Cavitation. This is the formation of vapor bubbles in the liquid being pumped, which can cause damage to the pump’s internal components. Cavitation is often caused by low net positive suction head (NPSH), which is the minimum pressure required to prevent cavitation.
- Misalignment. This is when the pump shaft is not aligned properly with the driver shaft. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration and wear, which can lead to premature failure of the pump.
- Bearing failure. The bearings in a pump help to support the rotating shaft and prevent it from rubbing against the pump housing. If the bearings fail, the shaft can rub against the housing, causing damage to both components.
- Seal failure. The seals in a pump prevent leakage of the pumped fluid. If the seals fail, the fluid can leak out of the pump, causing damage to the pump and the surrounding area.
- Corrosion. The pumped fluid can corrode the internal components of the pump, causing them to fail. Corrosion is often caused by the presence of acids or other corrosive chemicals in the fluid.
- Wear. The moving parts in a pump can wear over time, causing them to fail. Wear is often caused by the presence of abrasive particles in the fluid.
*Please note: a pump shaft and a pump coupling are not the same thing. A pump shaft is the rotating part of the pump that the impeller is attached to. A pump coupling is a device that connects the pump shaft to the motor shaft, and it allows for some misalignment between the two shafts.
Some additional tips for preventing positive displacement pump failures
- Use the correct pump for the application. Not all pumps are created equal, so it’s important to choose the right pump for the specific application.
- Operate the pump within its specified limits. Overloading or underloading the pump can cause premature failure.
- Maintain the pump regularly. This includes changing the oil and filters, inspecting the seals, and balancing the pump.
- Inspect the pump for signs of wear or damage. Regular inspections can help to identify potential problems before they cause a failure.
Positive displacement pump applications
- Transferring fluids between tanks or vessels
- Pressurizing fluids for use in hydraulic systems
- Metering fluids for precise dosing
- Dispensing fluids into containers
They are also well-suited for pumping fluids that are highly viscous, abrasive, or contain solids.

Summary
In conclusion, positive displacement pump is an important hydraulic transmission device with reliable and stable working performance and high pressure flow output capacity, which is widely used in many fields.
AOBL is a fluid transfer specialist, besides offering AODD and EODD, we also offer Sanitary Diaphragm Pumps, Filter Press Feed Pumps and Diaphragm Pump Parts & Accessories, we deal in Fluid Handling products and solutions to ensure your success, feel free to contact us.

